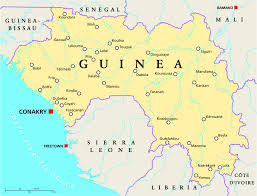
Guinea shares its northern border with Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, and Mali, and its southern border with Sierra Leone, Liberia, and Ivory Coast. The nation forms a crescent as it curves from its western border on the Atlantic Ocean toward the east and the south. The sources of the Niger River, Gambia River, and Senegal River are all found in the Guinea Highlands.
At 245,857 km2 (94,926 sq mi), Guinea is roughly the size of the United Kingdom. There are 320 km (200 mi) of coastline and a total land border of 3,400 km (2,100 mi). Its neighbours are Ivory Coast (Côte d'Ivoire), Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Senegal and Sierra Leone. It lies mostly between latitudes 7° and 13°N, and longitudes 7° and 15°W (a small area is west of 15°).
Guinea is divided into four main regions: Maritime Guinea, also known as Lower Guinea or the Basse-Coté lowlands, populated mainly by the Susu ethnic group; the cooler, mountainous Fouta Djallon that run roughly north-south through the middle of the country, populated by Fulas, the Sahelian Haute-Guinea to the northeast, populated by Malinké, and the forested jungle regions in the southeast, with several ethnic groups. Guinea's mountains are the source for the Niger, the Gambia, and Senegal Rivers, as well as the numerous rivers flowing to the sea on the west side of the range in Sierra Leone and Ivory Coast.
The highest point in Guinea is Mount Nimba at 1,752 m (5,748 ft). Although the Guinean and Ivorian sides of the Nimba Massif are a UNESCO Strict Nature Reserve, the portion of the so-called Guinean Backbone continues into Liberia, where it has been mined for decades; the damage is quite evident in the Nzérékoré Region at 7°32′17″N 8°29′50″W.
Regions and prefectures
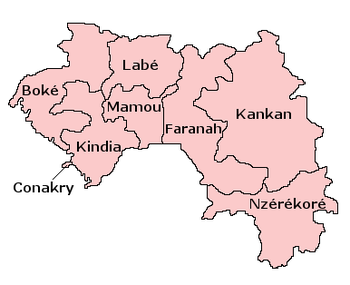
The Republic of Guinea covers 245,857 square kilometres (94,926 sq mi) of West Africa, about 10 degrees north of the equator. Guinea is divided into four natural regions with distinct human, geographic, and climatic characteristics:
- Maritime Guinea (La Guinée Maritime) covers 18% of the country.
- Middle Guinea (La Moyenne-Guinée) covers 20% of the country.
- Upper Guinea (La Haute-Guinée) covers 38% of the country.
- Forested Guinea (Guinée forestière) covers 23% of the country, and is both forested and mountainous.
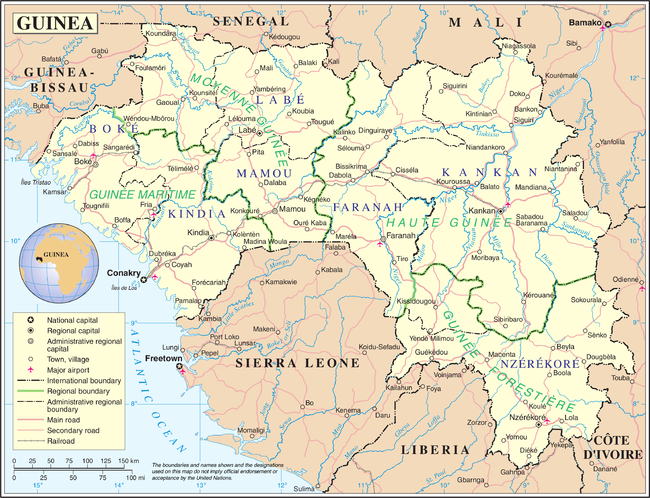
Guinea is divided into eight administrative regions and subdivided into thirty-three prefectures. Conakry is Guinea's capital, largest city, and economic centre. Nzérékoré, located in the Guinée forestière region in Southern Guinea, is the second largest city.
Other major cities in the country with a population above 100,000 include Kankan, Kindia, Labe, Guéckédou, Boke, Mamou and Kissidougou.
The capital Conakry with a population of 1,667,864 ranks as a special zone.
Source: Geography of Guinea